Want to map Farm Sustainability Index for your Region?
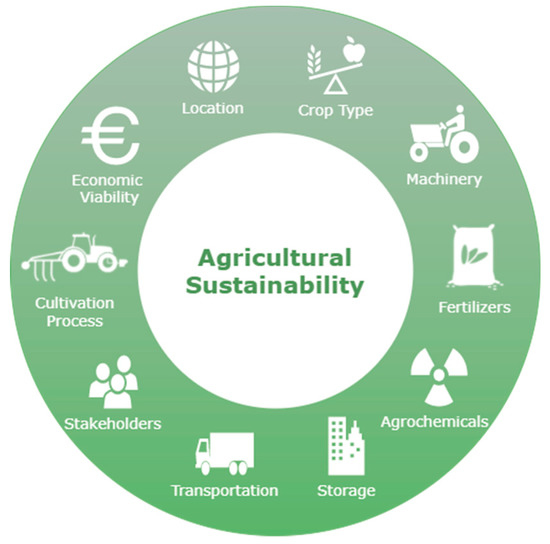
The Farm Sustainability Index (FSI) is a tool used to measure and track the sustainability of farming practices. The FSI evaluates a range of environmental, social, and economic indicators to assess the sustainability of a farm operation. The index is designed to help farmers, agricultural organizations, and policymakers make informed decisions about how to improve the sustainability of farming practices.
The FSI is based on the principle that sustainable farming practices must be environmentally sound, socially responsible, and economically viable. To measure sustainability, the FSI uses a combination of qualitative and quantitative indicators. Qualitative indicators include measures of soil health, biodiversity, and water quality, while quantitative indicators include measures of productivity, profitability, and resource use.
The Farm Sustainability Index (FSI) can be further enhanced by integrating satellite imagery and remote sensing data. Satellite imagery can provide detailed information on the environmental impact of farming practices, while remote sensing can help to track changes in crop productivity and resource use over time. Integrating these data sources with the FSI can provide a more comprehensive assessment of sustainability in agriculture.
Here are some ways in which satellite imagery and remote sensing can be used to enhance the FSI:
Soil health monitoring: Soil health is a key component of environmental sustainability in agriculture. Remote sensing can be used to monitor soil health indicators, such as soil moisture and organic matter content, over time. This can provide insights into the effectiveness of farming practices in maintaining or improving soil health.
Crop productivity and yield prediction: Satellite imagery can be used to monitor crop growth and predict crop yields. This can help farmers to optimize their crop management practices, improve productivity, and reduce waste. The FSI can incorporate these productivity and yield predictions to provide a more comprehensive evaluation of the economic sustainability of farming practices.
Water use efficiency: Water use efficiency is an important aspect of environmental sustainability in agriculture. Satellite imagery can be used to monitor water use patterns and track changes in water availability over time. This can help to identify areas where water use can be optimized and reduce the negative impact of farming practices on water resources.
Land use change detection: Remote sensing can be used to detect changes in land use patterns over time. This can provide insights into the effectiveness of land management practices and help to identify areas where improvements can be made. The FSI can incorporate this information to provide a more comprehensive evaluation of environmental sustainability.
By integrating satellite imagery and remote sensing data with the FSI, farmers, agricultural organizations, and policymakers can gain a more comprehensive understanding of the sustainability of farming practices. This can help to identify areas where improvements can be made and support the development of policies and programs that promote sustainable agriculture.